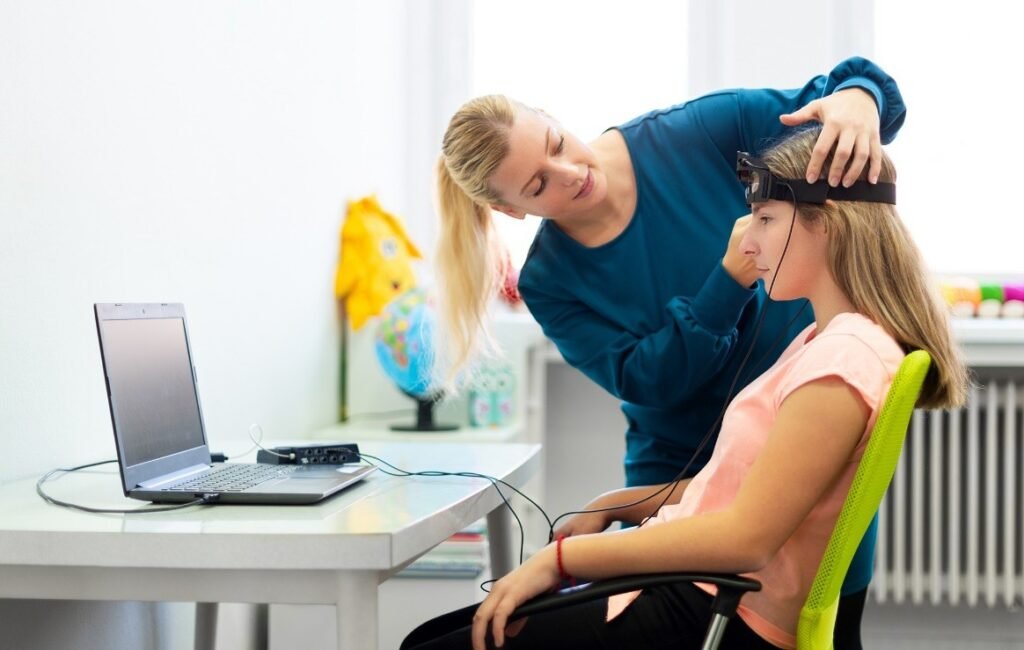
Neurofeedback is a form of brain-based training that helps people learn to regulate their own brain activity. It’s a type of biofeedback for the brain, using real-time information about brainwave patterns to encourage healthier, more balanced neural functioning.
Here's a clear, detailed breakdown of what Neurofeedback is and how it works:
What is Neurofeedback?
Neurofeedback (also called EEG biofeedback) uses sensors placed on the scalp to measure the brain’s electrical activity. A computer then displays this activity – often through graphs, sounds, or video animations – so the brain can “see itself” in action. With repeated practice, the brain learns to shift into more optimal patterns, much like physical exercise strengthens muscles.
Neurofeedback is noninvasive, painless, and does not involve putting electricity into the brain – it only measures naturally occurring electrical activity. In that way, it is similar to an electrocardiogram for your heart.
How it works
- Recording Brainwaves: Sensors pick up electrical signals from specific areas of the brain. These are translated into brainwave frequencies like those listed below. Then different symptoms can be linked to patterns – like excessive fast-wave activity in anxiety or too much slow-wave activity in ADHD.
- Delta (deep sleep)
- Theta (drowsy, daydreamy)
- Alpha (relaxed but alert)
- Beta (active, focused thinking)
- Gamma (high-level processing)
- Real-Time Feedback: The system gives the brain immediate feedback when it is moving into a more regulated state. This feedback could like like any of rewards listed below. The brain automatically learns from this feedback, reinforcing the helpful patterns.
- A movie brightening when the brain produces calm, focused waves
- A tone plays when the brain shifts into the desired pattern
- A video game responding to the brain’s activity
- Training Through Repetition: Over multiple sessions, the brain becomes better at:
- Staying calm under stress
- Maintaining focus
- Shifting out of “fight or flight”
- Regulating moods
This process is called operant conditioning, but applied at the level of neural activity.
What is Neurofeedback Used For?
It’s been applied to a wide range of issues, including:
- ADHD and attention regulation
- Anxiety and chronic stress
- PTSD and trauma-related symptoms
- Depression
- Sleep problems
- Migraines or tension headaches
- Emotional dysregulation
Some people also use it for peak performance, such as athletes, performers, and executives wanting to improve focus or stress resilience.
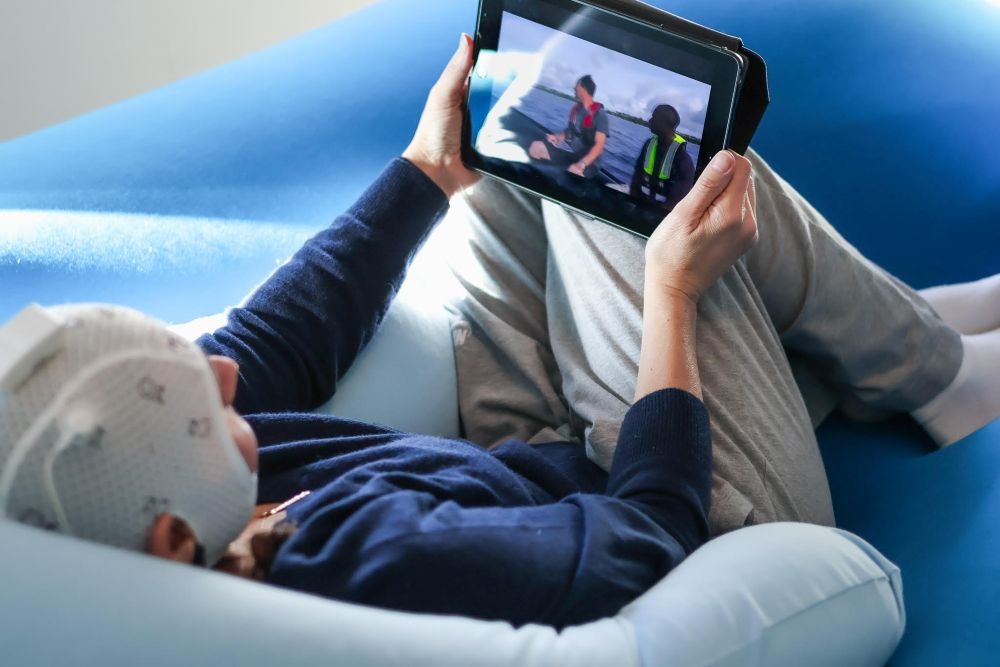

What it Feels Like
Most people describe it as:
- Relaxing
- Gentle
- Similar to meditation with coaching
- Sometimes mentally tiring (in a good way, like a workout)
Why Neurofeedback Works
Neurofeedback leverages the brain’s neuroplasticity – its natural ability to change and reorganize. By repeatedly guiding the brain toward healthier patterns, it gradually “re-tunes” itself, creating improvements in:
- Emotional stability
- Attention and cognitive clarity
- Stress tolerance
- Sleep quality
The changes are often long-lasting or permanent because the brain learns a new way of functioning, rather than relying on external tools.
What Does the Research Say About Neurofeedback?
Neurofeedback is supported by decades of neuroscience and clinical research demonstrating its effectiveness in improving brain regulation and mental health outcomes.
ADHD/Attention
- Neurofeedback for Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis — JAMA Psychiatry (2024) 🔗 https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamapsychiatry/fullarticle/2827733
- Clinical efficacy of neurofeedback protocols in ADHD 🔗 https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0925492723001336
PTSD & Trauma
- Neurofeedback effects on PTSD symptoms — systematic review & meta-analysis, Applied Psychophysiology & Biofeedback (moderate effect size). 🔗https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/37314616/
-
Updated PTSD neurofeedback review (2024) — Frontiers in Psychiatry (larger evidence base with multiple clinical outcomes).
🔗https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38577405/
Mood, Depression, Anxiety & Emotion Regulation
-
fMRI-based neurofeedback for depression — systematic review showing clinically meaningful change.
🔗https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/40660681/ -
Review of neurofeedback for mood & anxiety disorders — NCBI Bookshelf summary of clinical effects.
🔗https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK531603/
Sleep & Insomnia
-
Neurofeedback and sleep quality meta-analysis — Frontiers in Neuroscience (review of randomized clinical trials).
🔗https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/39568666/ -
Specific RCT — alpha neurofeedback for insomnia — Psychiatry Research randomized trial (ongoing publication).
🔗https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/39946965/
For more information, please contact us.
Nina McCormack, LCSW, is licensed in Virginia, Pennsylvania, Maryland, and Washington, DC.